A Study on Yangsaeng in Korean Elders
Article information
Abstract
Purpose
This study was to survey yangsaeng in Korean elders.
Methods
A total of 250 subjects aged between 60 and 88 were selected through convenient sampling. Data were collected with a self-reported questionnaire from April 1 to 30, 2009. Collected data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN 15.0.
Results
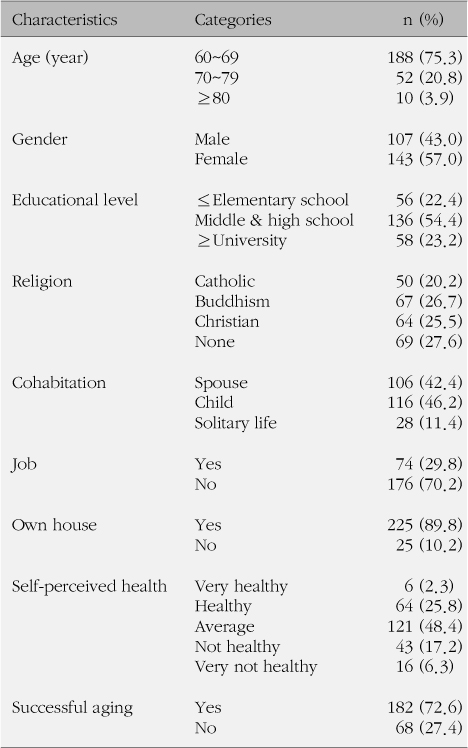
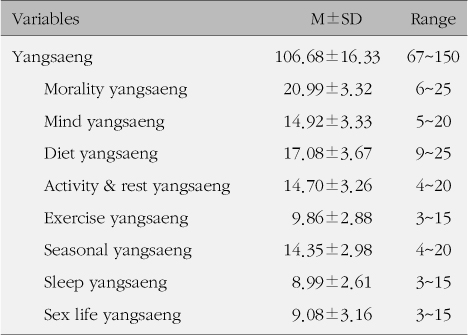
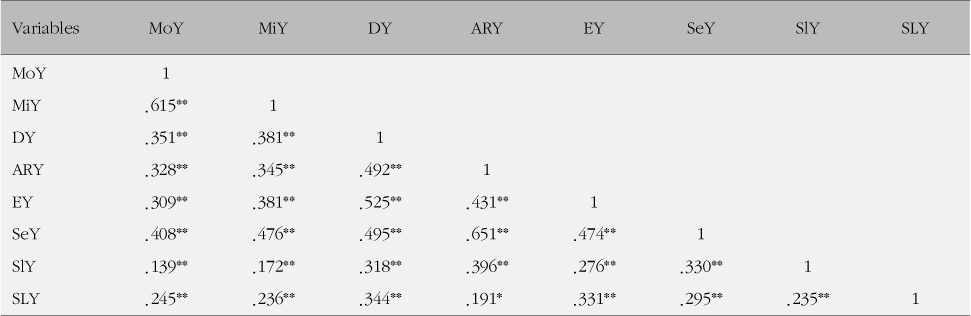
Differences in yangsaeng according to general characteristics were as follows. Total yangsaeng and all of yangsaeng categories except seasonal yangsaeng were significantly different according to self-perceived health. Diet yangsaeng was significantly different according to cohabitation, house ownership and self-perceived health. Activity and rest yangsaeng was significantly different according to age, gender, job, successful aging and self-perceived health. Exercise yangsaeng was significantly different according to gender and self-perceived health. Seasonal yangsaeng was significantly different according to successful aging and self-perceived health. Sleep yangsaeng was significantly different according to age, gender, job and self-perceived health. Sex life yangsaeng was significantly different according to all of the variables except religion and successful aging. There was a positive correlation between yangsaeng and the variables.
Conclusion
The findings of this study may be useful in understanding the health status of community-dwelling elders and developing more specific health promotion programs.
Notes
This study was supported by the Kaya University Research Fund in 2010.