Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs > Volume 23(3); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP) on Depression and Quality of Life among Community-dwelling Korean Elderly Persons
- Hung Sa Lee, Chunmi Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing 2012;23(3):338-346.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2012.23.3.338
Published online: September 30, 2012
1Department of Nursing, Daegu Haany University, Daegu, Korea.
2Department of Nursing, Sunmoon University, Asan, Korea.
Copyright © 2012 Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing
- 263 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to examine the association between oral health impact profile, depression and quality of life among community-dwelling elderly persons in South Korea.
-
Methods
- The design of this research was cross-sectional descriptive study. The participants were 266 community-dwelling individuals aged 65 and older. Data were collected from November 20 to December 20, 2011. The measurements for assessing the subjects' oral health, depression, quality of life were OHIP-14, GDS-SF and QOL. Data were collected using self-administered or interviewer-administered questionnaires. Collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation coefficient and stepwise multiple regression.
-
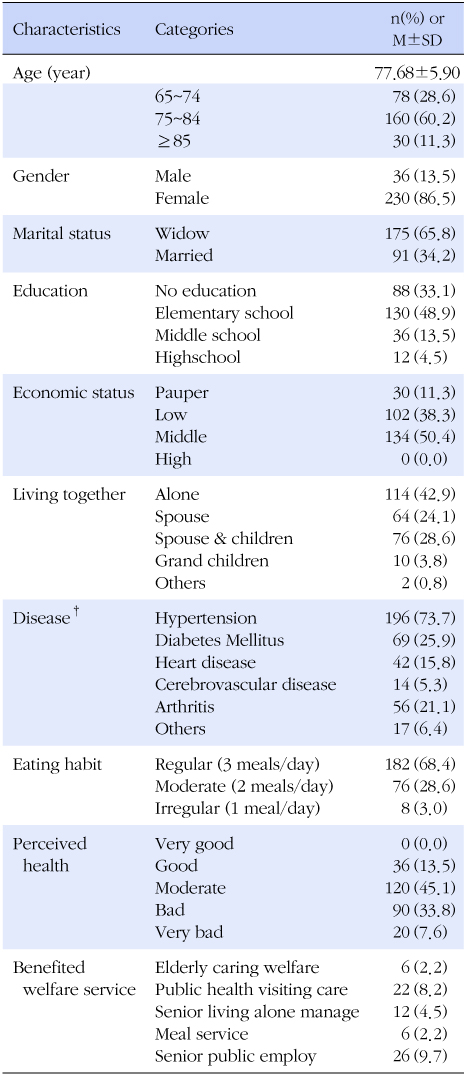
Results
- The participants' mean age was 77.68, and 86.5% were female, 42.9% were living-alone elders. Pearson's correlation coefficient analysis found that oral health impact profile was significantly associated with depression (r=-.622, p<.001), QOL (r=-.400, p<.001), number of disease (r=.298, p<.001), age (r=.198, p=.002), education (r=-.149, p=.015), eating habit (r=.185, p=.003). The QOL was explained 54.7% by depression (β=-.619), oral health impact profile (β=-.127), number of benefited welfare service (β=.235), perceived health (β=-.327), eating habit (β=-.094) using stepwise multiple regression analysis.
-
Conclusion
- These results indicate that the intervention program of oral health promotion for community-dwelling elders is needed from now on.
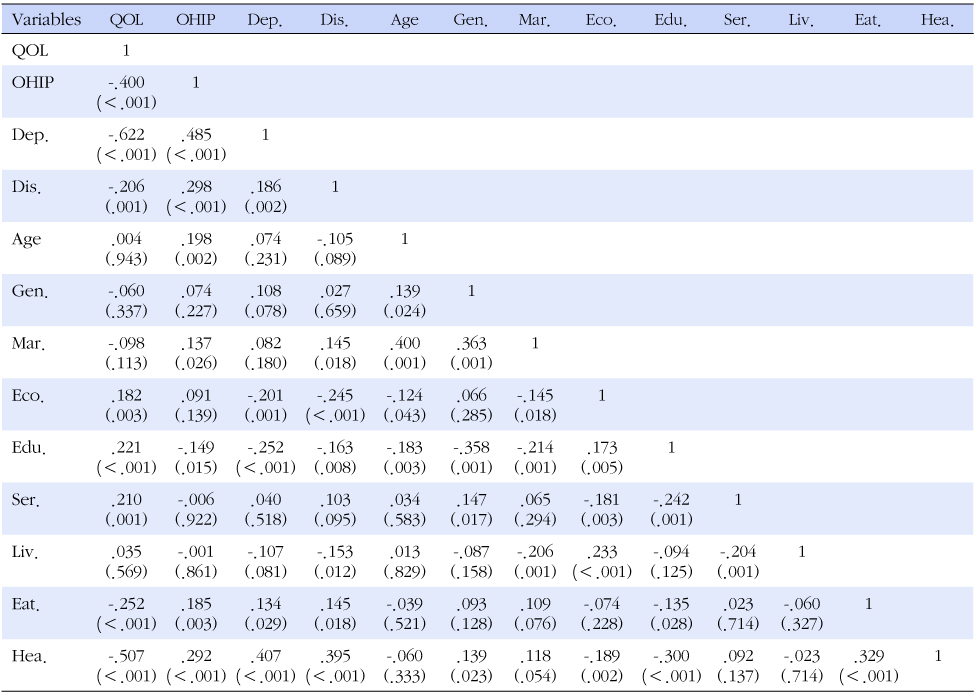
Note. p-value calculated by Pearson's correlation.
QOL=quality of life; OHIP=oral health impact profile; Dep.=depression; Dis.=number of disease; Gen.=gender;, Mar.=marital status; Eco.=economic status; Edu.=education; Ser.=number of benefited welfare service; Liv.=living together; Eat.=eating habit; Hea.=perceived health.

Note. p-value calculated by stepwise multiple regression, independent variables are entered if F≥3.840, p<.05; Perceived health (1=good, 2=moderate, 3= bad, 4=very bad), Eating habit (1=regular, 2=moderate, 3=irregular), Education (1=no education, 2=elementary school, 3=middle school, 4=high school), Economic status (1=pauper, 2=low, 3=middle, 4=high).
- 1. Back JU. The effect of oral health on total health and quality of life between Korean and Japanese. Korean Public Health Res 2012;38(1):81–98.
- 2. Bae KH, Kim HD, Jung SH, Park DY, Kim JB, Paik DI, et al. Validation of the Korean version of the oral health impact profile among the Korean elderly. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2007;35:73–79.
- 3. Griffin SO, Jones JA, Brunson D, Griffin PM, Bailey WD. Burden of oral disease among older adults and implications for public health priorities. Am J Public Health 2012;102(3):411–418.
- 4. Ho APY. A peer counselling program for the elderly with depression living in the community. Aging Ment Health 2007;11(1):69–74.
- 5. Jang YR, Chiriboga DA, Kim GY. Acculturation and manifestation of depressive symptoms among Korean American older adults. Korean J Res Gerontol 2006;15:51–73.
- 6. Jensen PM, Saunders RL, Thierer T, Friedman B. Factors associated with oral health-related quality of life in community-dwelling elderly persons with disabilities. J Am Geriatr Soc 2008;56(4):711–717.
- 7. Kim HK, Lee HJ, Park SM. Factors influencing quality of life in elderly women living alone. J Korean Gerontol Soc 2010;30(2):279–292.
- 8. Lee EH. Instruments for health related quality of life. Korean J Nurs Query 2007;16(2):24–38.
- 9. Lee GR. The impact of DMFT index on oral health related quality of life in community-dwelling elderly. J Korean Acad Dent Health 2008;32(3):396–404.
- 10. Lee HS, Kim DK, Ko HJ, Ku HM, Kwoon EJ, Kim JH. The standardization of 「Geriatric Quality of Life scale」. Korean J Clin Psychol 2003;22(4):859–881.
- 11. Lee MS, Kim SH, Yang JS, Oh JS, Kim DK. Validity and reliability of the oral health impact profile in elderly Korean 65+. Korean Acad Dent Health 2005;20(2):210–221.
- 12. Lee SA, Lee GM. A study on the major factors influencing the depression among the elderly in rural area. J Korea Gerontol Soc 2002;22(1):209–226.
- 13. Lim YM. Effect of movement exercise on physical and emotional functioning in elders with cognitive impairments. J Korea Gerontol Soc 2002;21(3):197–211.
- 14. Lin MR, Wolf SL, Hwang HF, Gong SY, Chen CY. A randomized, controlled trial of fall prevention program and quality of life in older fallers. J Am Geriatr Soc 2007;55(4):499–506.
- 15. Lin QL, Kim HK, Ann JS. Relationship between depression and quality of life in elderly women living alone: The moderating and mediating effect of social support and social activity. J Korean Gerontol Soc 2011;31(1):33–47.
- 16. Locker D, Matear D, Stephens M, Lawrence H, Payne B. Comparison of the GOHAI and OHIP-14 as measures of the oral health-related quality of life of the elderly. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2001;29:373–381.
- 17. Loughlin A. Depression and social support effective treatments for homebound elderly adults. J Gerontol Nurs 2004;30(5):11–15.
- 18. Nam KM, Jung EK. The influence of social activity and social support perceived by elderly women living alone on their quality of life: Focusing on the mediating effect of depression and death-anxiety. J Welf Aged 2011;52:325–348.
- 19. Panchbhai AS. Oral health care needs in the dependant elderly in India. Indian J Palliat Care 2012;18(1):19–26.
- 20. Park MS, Choi SM. The effects of oral care education on caregivers' knowledge, attitude, & behavior toward oral hygiene for elderly residents in a nursing home. J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(5):684–693.
- 21. Park MS, Ryu SA. Degree of dry mouth and factorsinfluencing oral health-related quality of life for community-dwelling elders. J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(5):747–755.
- 22. Park SY. A study on depression, ADL, IADL, and QOL among community dwelling, low income elderly. J Korean Acad Public Health Nurs 2009;23(1):78–90.
- 23. Roberts J. Developing an oral assessment and intervention tool for older people: 3. Br J Nurs 2000;9(19):2073–2078.
- 24. Ryu KJ, Lee TY, Kim KY. A study on oral health-related quality of life of among elderly in metropolis. J Korean Acad Dent Hyg Educ 2009;9(4):620–632.
- 25. Slade GD. Derivation and validation of a short-form oral health impact profile. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1997;25:284–290.
- 26. Yoon HS, Chun JH, Lee JH. Oral health and self-rated health among the elderly in Busan. J Dent Hyg Sci 2012;12(3):197–207.
- 27. Yoon YS. A study on oral health related quality of life in elders concerning to residence at urban and rural. J Dent Hyg Sci 2006;6(1):23–28.
- 28. Zini A, Sgan-Cohen HD. The effect of oral health on quality of life in an underprivileged homebound and non-homebound elderly population in Jerusalem. J Am Geriatr Soc 2008;56:99–104.
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 KACHN
KACHN
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

