Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs > Volume 23(1); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Effects of Lifestyle Factors on Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adults
- Mee Young Im, Young-Ran Lee, Suk Jung Han, Chung-Min Cho
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing 2012;23(1):13-21.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2012.23.1.13
Published online: March 31, 2012
1Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Seoil College, Seoul, Korea.
2Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Seoul Women's College of Nursing, Seoul, Korea.
3Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Samyook University, Seoul, Korea.
4Professor, Department of Nursing, Sungshin Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
• Received: February 10, 2012 • Revised: March 21, 2012 • Accepted: March 21, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing
- 781 Views
- 3 Download
- 21 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to estimate the effects of lifestyle factors on metabolic syndrome (MS) among Korean adults (age≥20).
-
Methods
- A total of 7,798 subjects (weighted subjects=37,215,961) were recruited from the 2009 Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-3). Data were analyzed by t-test, χ2-test, and logistic regression in consideration of strata, cluster and weight as national data using the SAS 9.1 program.
-
Results
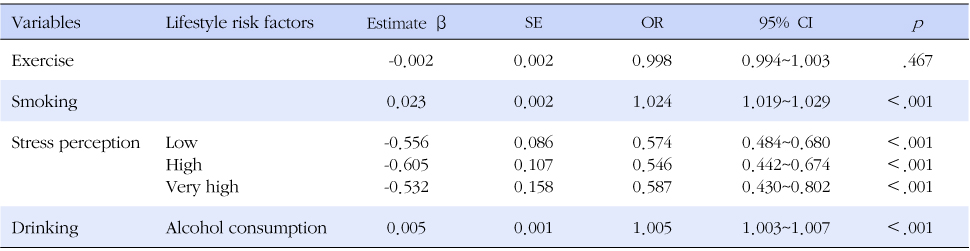
- The prevalence of MS by definition of AHA/NHLBI and waist circumference cutoff points for Koreans was 22.4%. The mean clinical MS score for MS patients was 3.4, but the mean score for the non-MS group was 1.2 out of 5.0. Among the lifestyle factors, smoking (OR=1.024), stress (0.546≤OR≤0.587) and drinking (OR=1.005) had significant influence on the MS risk and MS scores, but exercise did not.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study indicate that further research is necessary on the effect of lifestyle factors on MS risk and nurses should focus on effective programs about smoking, stress and drinking for the prevention and reduction of MS risk.
Table 1Comparison of Demographic Characteristics between MS and Non-MS Groups (N=7,798, wN=37,215,961)
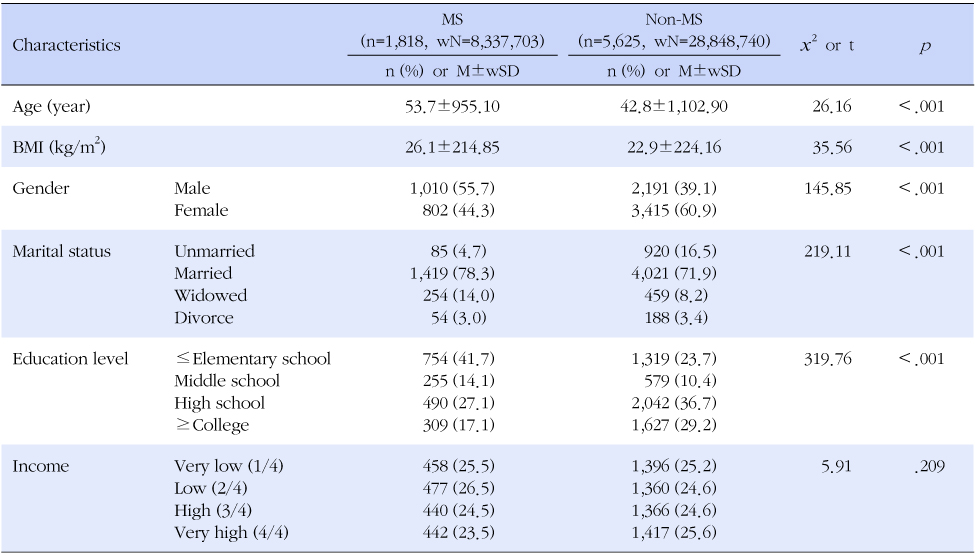

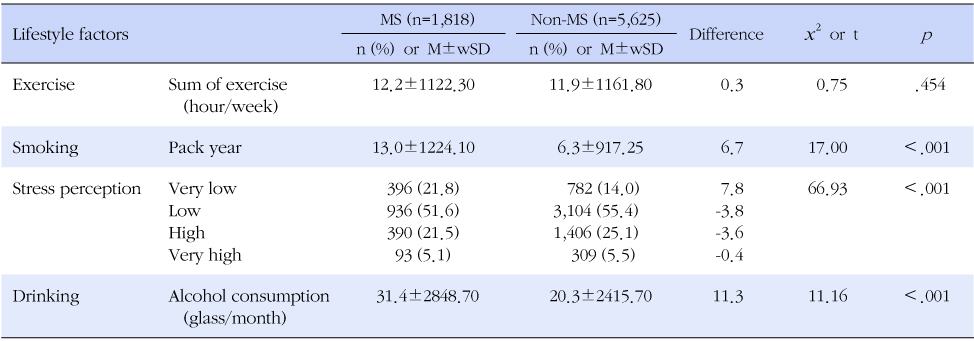
Table 2Comparison of Metabolic Syndrome Clinical Determinants between MS and Non-MS Groups (N=7,798, wN=37,215,961)


- 1. American Heart Association. Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP): Expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III) final report. Circulation 2002;106:3143–3421.
- 2. Azadbakht L, Mirmiran P, Esmaillzadeh A, Azizi T, Azizi F. Beneficial effects of a dietary approaches to stop hypertension eating plan on features of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2005;28:2823–2831.
- 3. Choi JH, Park S, Shin YH, Kim MY, Lee YJ. Sex differences in the relationship between metabolic syndrome and pulmonary function: The 2007 Korean national health and nutrition examination survey. Endocr J 2011;58:459–465.
- 4. Eckel RH, Barouch WW, Ershow AG. Report of the national heart, lung, and blood institute-national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases working group on the pathophysiology of obesity-associated cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002;105:2923–2928.
- 5. Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: Findings from the third national health and nutrition examination survey. JAMA 2002;287:356–359.
- 6. Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: Emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:677–685.
- 7. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005;112:2735–2752.
- 8. Hong AR, Lee KS, Lee SY, Yu JH. Association of current and past smoking with metabolic syndrome in men. J Prev Med Public Health 2009;42(3):160–164.
- 9. Jung CH, Park JS, Lee WY, Kim SW. Effects of smoking, alcohol, exercise, level of education, and family history on the metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Korean J Med 2002;63:649–659.
- 10. Kim MH, Kim MK, Choi BY, Shin YJ. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and its association with cardiovascular diseases in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2004;19:195–201.
- 11. Kim YH, Yang YO. Effects of walking exercise on metabolic syndrome risk factors and body composition in obese middle school girls. J Korean Acad Nurs 2005;35:858–867.
- 12. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-3) 2009;Seoul: Author.
- 13. Lee HS, Kwon CS. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and related risk factors of elderly residents in Andong rural area: 1. Based on the anthropometric measurements and health behaviors. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 2010;39:511–517.
- 14. Lee SY, Park HS, Kim DJ, Han JH, Kim SM, Cho GJ, et al. Appropriate waist circumference cutoff points for central obesity in Korean adults. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007;75:72–80.
- 15. Lim S, Jang HC, Lee HK, Kim KC, Park C, Cho NH. A rural-urban comparison of the characteristics of the metabolic syndrome by gender in Korea: The Korean Health and Genome Study (KHGS). J Endocrinol Invest 2006;29:313–319.
- 16. Ministry of Health, Welfare and Family Affairs. The Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III) 2005 -health examination- 2008;Retrieved March 20, 2012. from http://dl.nanet.go.kr/OpenFlashViewer.do
- 17. Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP): Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001;285:2486–2497.
- 18. Oh EG, Bang SY, Hyun SS, Chu SH, Jeon JY, Kang MS. Knowledge, perception and health behavior about metabolic syndrome for an at risk group in an rural community area. J Korean Acad Nurs 2007;37:790–800.
- 19. Park HS, Lee SY, Kim SM, Han JH, Kim DJ. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among Korean adults according to the criteria of the International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Care 2006;29:933–934.
- 20. Park HS, Oh SW, Cho SI, Choi WH, Kim YS. The metabolic syndrome and associated lifestyle factors among South Korean adults. Int J Epidemiol 2004;33:328–336.
- 21. Reaven GM. Banting lecture: Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988;37:1595–1607.
- 22. Shim HS, Kim HS, Kim JH. Analysis of metabolic syndrome risk factors among the menopausal women in her fifties. J Korean Biol Nurs Sci 2010;12:58–62.
- 23. Tak YR, An JY, Kim YA, Woo HY. The effects of a physical activity-behavior modification combined intervention (PABM-intervention) on metabolic risk factors in overweight and obese elementary school children. J Korean Acad Nurs 2007;37:902–913.
- 24. Yoo JS, Jeong JI, Park CG, Kang SW, Ahn JA. Impact of life style characteristics on prevalence risk of metabolic syndrome. J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39:594–601.
- 25. Yoon YS, Oh SW, Baik HW, Park HS, Kim WY. Alcohol consumption and the metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: The 1998 Korean national health and nutrition examination survey. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;80:217–224.
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Lifestyle and Health Behaviors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease
Goeun Chung, Hye-Jin Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2024; 22(2): 105. CrossRef - Effects of Oral Health Behavior and Mental Health on Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, Sang-Eun Moon, Sun-Hwa Hong
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2022; 22(2): 90. CrossRef - Sociodemographic and Health Characteristics Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Men and Women Aged ≥50 Years
Goeun Chung, Hye-Sun Jung, Hye-Jin Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(3): 159. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Development of Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households: A Sex-Stratified Analysis
Jui Kim, Hyoungshim Choi
Sustainability.2021; 13(16): 9032. CrossRef - The Effect of Depression on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components among Korean Adults
Mee Young Im
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2021; 29(4): 235. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Among Middle-Aged Women in Their 50s: Based on National Health Screening Data
HyungSeon Kim, YeonHee Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3008. CrossRef - The Effect of Stress on Prevalence Risk of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adults
Mee Young Im
STRESS.2019; 27(4): 441. CrossRef - Development of tailored contents of a mobile health application to prevent the metabolic syndrome
Jiye Kim, Jiwan Kang, Harim Kim, Juyeun Ko, Hyekyeong Kim, Yuri Kim, Kwangsuk Ko, Minsoo Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2018; 35(3): 25. CrossRef - Factors affecting metabolic syndrome by lifestyle
Nam-Kyun Ki, Hae-Kag Lee, Jae-Hwan Cho, Seon-Chil Kim, Nak-Sang Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2016; 28(1): 38. CrossRef - Correlations between metabolic syndrome, serologic factors, and gallstones
Jae Hong Sang, Nam Kyun Ki, Jae Hwan Cho, Jae Ouk Ahn, Jae Gun Sunwoo
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2016; 28(8): 2337. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Readability and Suitability of Printed Educational Materials on Metabolic Syndrome
Jung Eun Kim, Sook Ja Yang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(1): 149. CrossRef - The Effects of Menopause on the Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Women
SoYoun Bang, IlGu Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(4): 2704. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence and Lifestyle by Age and Metabolic Syndrome Status in Women Religious
Yang-Hee Kim, Hee-Seung Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2015; 17(1): 11. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Literature on Community Health Center Exercise Programs
Suk-Jung Han, Young-Ran Lee, Chung-Min Cho, Mee-Young Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(1): 18. CrossRef - Assessment of Nurses' Nutritional Knowledge and Educational Needs Regarding Stroke Specific Diet Regimens
Suk-Hee Song, Smi Choi-Kwon, Ji Hyun Baek, Kuyng-Ja Song, Chi-Kang Koh
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2015; 17(3): 228. CrossRef - The Effects of Metabolic Syndrome on Quality of Life
So Youn Bang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(10): 7034. CrossRef - Nutrition Knowledge, Food Habit Problems and Dietary Attitudes of Nursing Students
Su-Ol Kim, So-Myeong Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(4): 466. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Metabolic Syndrome Prevention Program for University Students using Mobile Application.
Han Kyu Kang, Tae Bin Kim, Kyu Hyung Kim, Min Jin Kim, Jin Hyun Kim, Hyun Yong Kim, Kyung Hoon Yeom, Ka Hyun Lee, Eun Young Choi, Kyung Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(3): 205. CrossRef - The Effects of Lifestyle Factors on Metabolic Syndrome among Adolescents
Hanju Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(2): 270. CrossRef - Discriminating Factors of Stages of Change for Exercise among Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Hyun Ju Hwang, Eun Nam Lee, Eun Jung Choi
Journal of muscle and joint health.2014; 21(1): 46. CrossRef - Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome and Its associated Factors among Elders in a Rural Community
Bongjeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(2): 225. CrossRef

 KACHN
KACHN
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

